How 3D Printing Accelerates Rapid Prototyping and Functional Mockup Processes
In product development, speed means opportunity. When a design moves from paper to physical form, rapid prototyping and functional mockups become indispensable steps for every hardware team, industrial design firm, and manufacturing enterprise. In recent years, the rise of 3D printing technology has been reshaping this process with unprecedented efficiency.
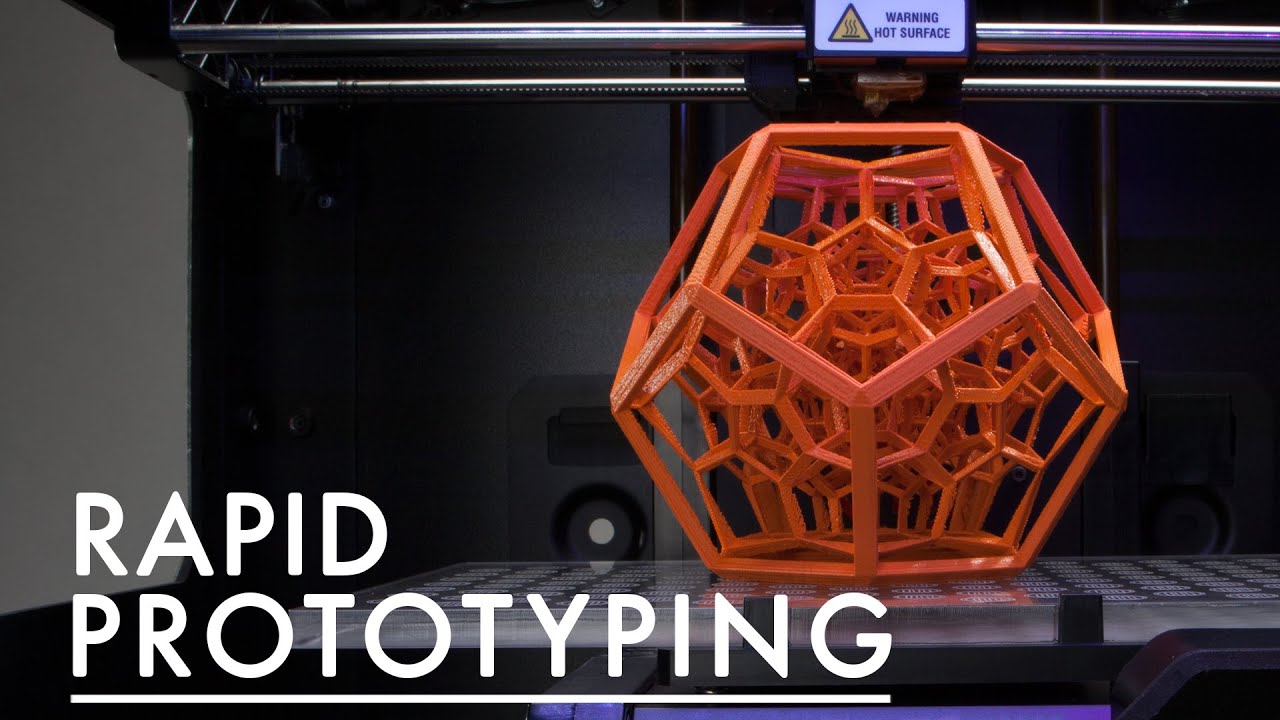
Whether you are a startup founder or an experienced engineer or designer, if you are still relying on traditional prototyping methods, you may already be a step behind. This article will systematically explain why more and more companies choose 3D printed prototypes, what 3D printing technologies are available, which ones are best suited for rapid prototyping, and—most importantly—how to choose the right prototyping method in 2025 to seize the lead in product iteration.
What Are Rapid Prototyping and Functional Mockups?
Before diving in, let’s clarify a few concepts:
- Rapid Prototyping: The process of quickly producing a product model from digital designs, mainly to validate structure, function, and assembly.
- Functional Mockup: A specific form of rapid prototyping where a physical model closely resembling the final product is created for testing, demonstration, or small batch pilot production.
- 3D Printing: One of the most popular means to achieve rapid prototyping, offering mold-free, flexible, and efficient production—especially suitable for small batches and diverse needs.
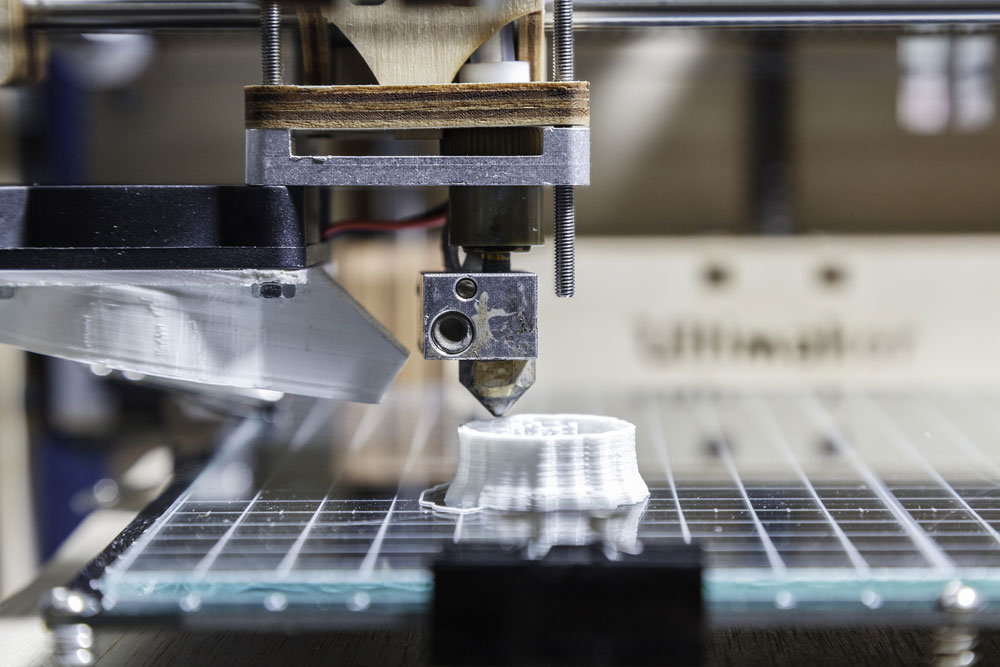

Traditional CNC machining offers high precision but involves significant programming time and cost. Silicone molding suits batch production but lacks flexibility. Compared to these, 3D printing has nearly no barriers, supports complex geometries and various materials, and aligns perfectly with today’s fast trial-and-error development approach.
Why Are More Companies Choosing 3D Printed Prototypes?
This is not just a “convenience” choice, but a necessity driven by competition.
- No tooling required, lower upfront cost
For startups frequently changing designs, tooling costs are a trap. 3D printing creates parts on demand—modify your design and print immediately without mold constraints. - Supports complex structures with high design freedom
Traditional methods are limited by tool paths or mold shapes. 3D printing enables freeform geometry, ideal for complex shapes, hollow parts, and skeletal supports. - Short turnaround, from drawing to sample in as fast as 24 hours
Using SLA resin printing, white models can reach ±0.1mm accuracy with smooth surfaces, perfect for visual verification. Through Leanplans online platform, uploading 3D files yields instant quotes and same-day production starts.
Mainstream 3D Printing Technologies: Which Fits Your Needs?
Common 3D printing methods for prototyping include:
| Technology | Principle | Advantages | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| SLA | Photopolymer curing | High precision, smooth finish | Visual models, transparent parts, displays |
| SLS | Nylon powder sintering | Strong, no support structures needed | Structural parts, clips, functional testing |
| MJF | Multi-jet fusion | Fast build, fine details | Small batch pilot runs, functional components |
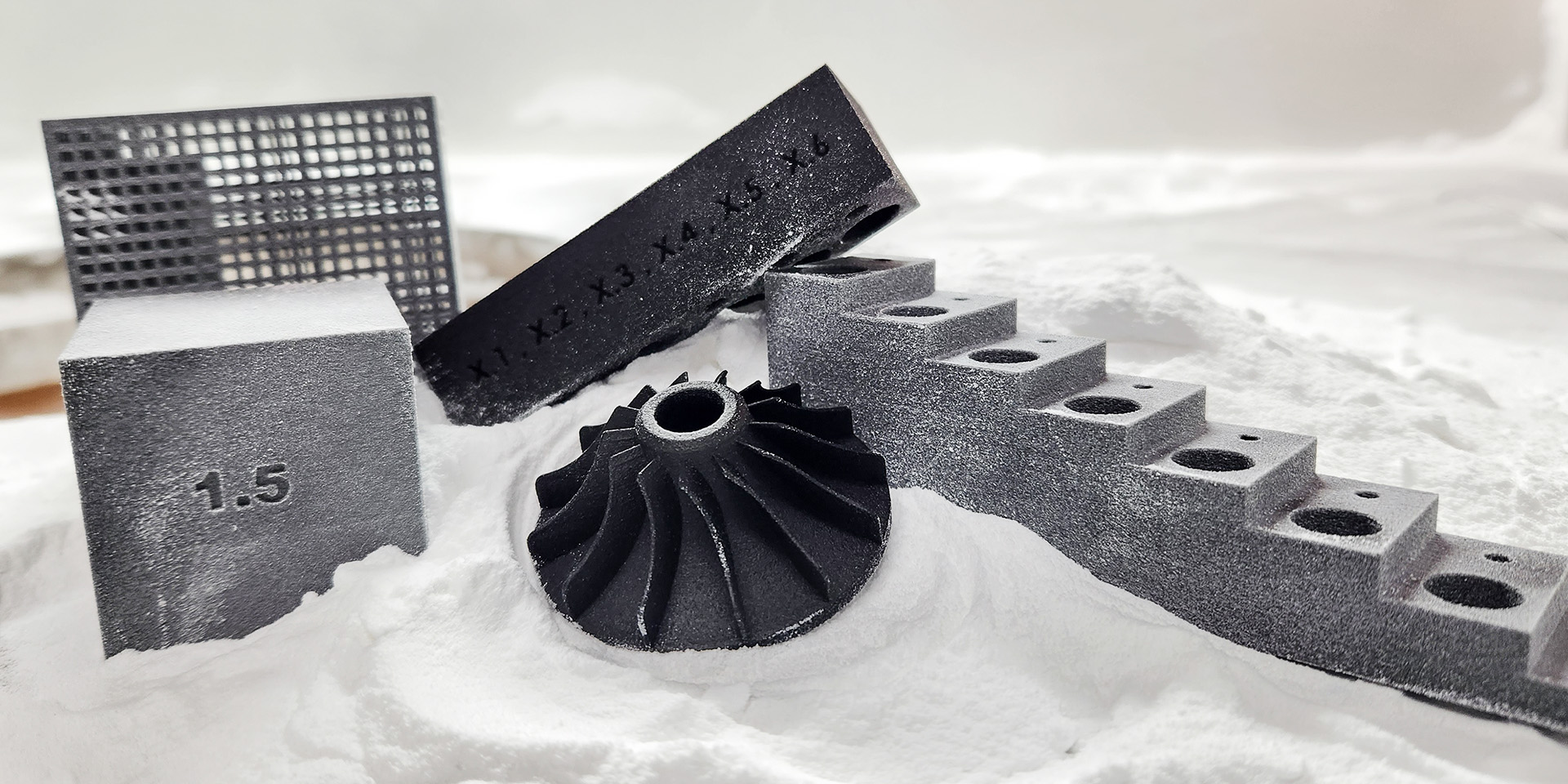

If unsure which to choose, consider SLA for shape verification, SLS for structural testing, and MJF for functional and production-ready parts. Beyond these, metal 3D printing (SLM/EBM) represents a high-value, technically advanced option increasingly used in rapid prototyping.
Metal 3D Printing Breaks New Ground
Previously, metal prototypes depended on CNC machining or casting—both costly and limited, especially for hollow, heat-dissipating, or lattice structures that are hard to form in one piece. Metal 3D printing overcomes these:
High precision microstructures: SLM laser melting with 50μm layer thickness meets precision mechanical needs
Material diversity: Stainless steel, aluminum alloys, titanium, Inconel high-temp alloys, etc.
Functional use: Printed metal parts approach forging strength, enabling direct end-use testing or short-term applications
With domestic metal printers and lower powder costs, metal 3D printing is no longer exclusive to aerospace. More hardware startups now prototype motor housings, module brackets, and connectors with this technology.
Right Materials Make Prototyping More Effective
Choosing the right material often matters more than the process. 3D printing materials affect both appearance and whether samples can be used for functional or end-use testing. Common prototyping materials include:
Non-metal materials (SLA/SLS/MJF):
| Material Type | Supported Process | Characteristics | Application Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Photopolymer Resin | SLA | Smooth surface, high transparency | Visual models, display parts, medical models |
| White Resin (ABS-like) | SLA/MJF | ABS-like strength, paintable | Housings, structural parts, assembly verification |
| Nylon 12 (PA12) | SLS/MJF | High strength, wear-resistant, tough | Functional structural parts, small batch production |
| Elastomers (TPU/TPE) | SLS | Compressible, flexible, rubber-like | Covers, protective pads, flexible connectors |
Metal materials (SLM/EBM):
| Material | Characteristics | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel (316L) | Corrosion resistant, strong, machinable | Fixtures, mechanical housings |
| Aluminum Alloy (AlSi10Mg) | Lightweight, good heat dissipation | Heat sinks, lightweight covers |
| Titanium Alloy (Ti6Al4V) | High strength-to-weight, heat resistant | Aerospace parts, medical implants |
| Inconel 718 | High-temp corrosion resistance | Engine parts, high-temp modules |
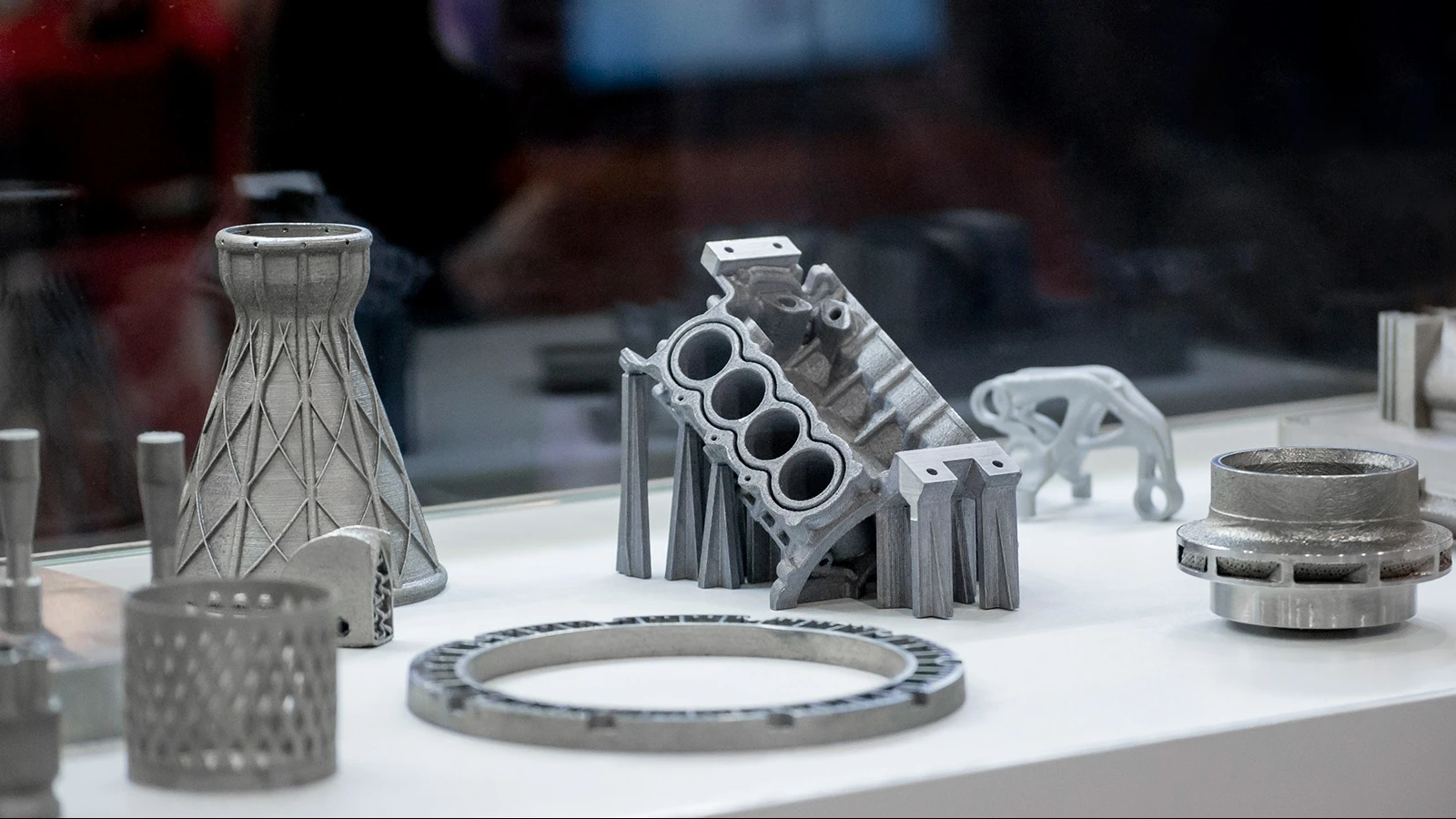

Material Selection Tips:
For visual display: photopolymer or white ABS-like resin
For structural validation: PA12 nylon or black/white MJF resin
For flexible parts/covers: TPU elastomer
For functional testing: metal prints like 316L stainless steel or titanium
AI + 3D Printing: Prototyping Enters the Smart Era
Traditional prototyping workflows—design → structural confirmation → material selection → sourcing multiple vendors → manual communications → quoting → ordering → production → quality control → delivery—take weeks to a month.
Today, AI-driven rapid prototyping solutions drastically shorten this. From file upload, Leanplans’ AI multi-agent “experts” automatically:
Analyze structure complexity and generate DFM reports
Recommend suitable processes (SLA, SLS, etc.)
Suggest appropriate materials (ABS-like, nylon, elastomers, etc.)
Generate quotes and delivery times in 5 seconds for instant ordering
What does this mean? Your designer sketches in the morning, sees a physical model by evening, and can present it in a review meeting the next day. This speed is the ultimate goal for hardware innovators today.
Speed of Prototyping = Accelerator of Product Success
The era of “slow and precise” is over. Speed and flexibility are the true weapons of hardware innovation, and 3D printing is the “turbocharger” in this race.
If you want to go from idea to market faster, rethink your prototyping method. Are you still waiting in production queues? Are high tooling costs blocking your iterations?
It’s time to try a one-stop 3D printing prototyping platform. Upload your files, get smart quotes, and receive rapid delivery—all starting within minutes. Let 3D printing be the first step toward your product’s success.
Get a Free Quote!
Leave your contact details, or directly visit our online quoting platform to experience the future of material selection and production. Get expert material evaluations, tailored DFM analysis, and fast 24-hour production turnaround.
- Free Quote: Upload your designs, and our AI-powered engine will generate a custom quote in seconds.
- Talk to an Expert: Connect with one of our engineers via WhatsApp for immediate assistance.

